Novel method for composite production with injection compression moulding
We demonstrate the feasibility and relevance of a novel composite production method, thermoplastic compression resin transfer moulding (TP-CRTM) coupled with injection compression moulding.
- Fibre-reinforced plastics
- Variothermal injection compression moulding
- TP-CRTM
- FEA
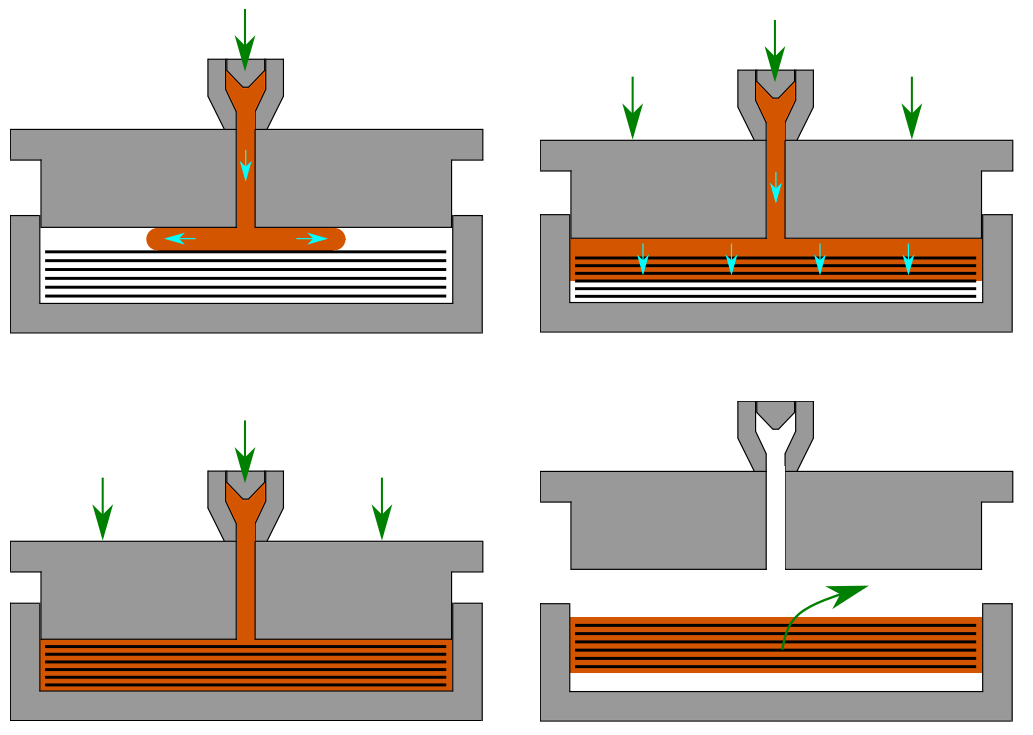
Using fibre reinforced thermoplastics in the mobility sector can considerably reduce weight and therefore fuel consumption. Their manufacture is as of today mainly based on expensive semi-finished materials, preventing their broad use such as in the automotive industry. Alternative manufacturing routes are therefore sought to reduce the costs and enable a broader use of these composites. One promising technology is thermoplastic compression resin transfer moulding coupled with injection compression moulding and low-viscosity thermoplastics. However, its implementation at an industrial scale remains challenging mainly because of difficult cavity sealing.
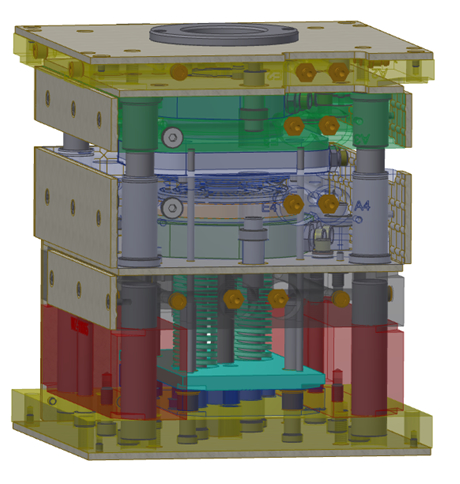
The main goal of the project is to design and build a mould specifically designed to overcome the difficulties of cavity sealing in a variothermal environment. Appropriate process parameters are experimentally defined to produce a fully consolidated composite with short processing times. Finally, the produced parts are mechanically characterized to prove the relevance of the process. Guidelines on how to define robust process parameters are presented.
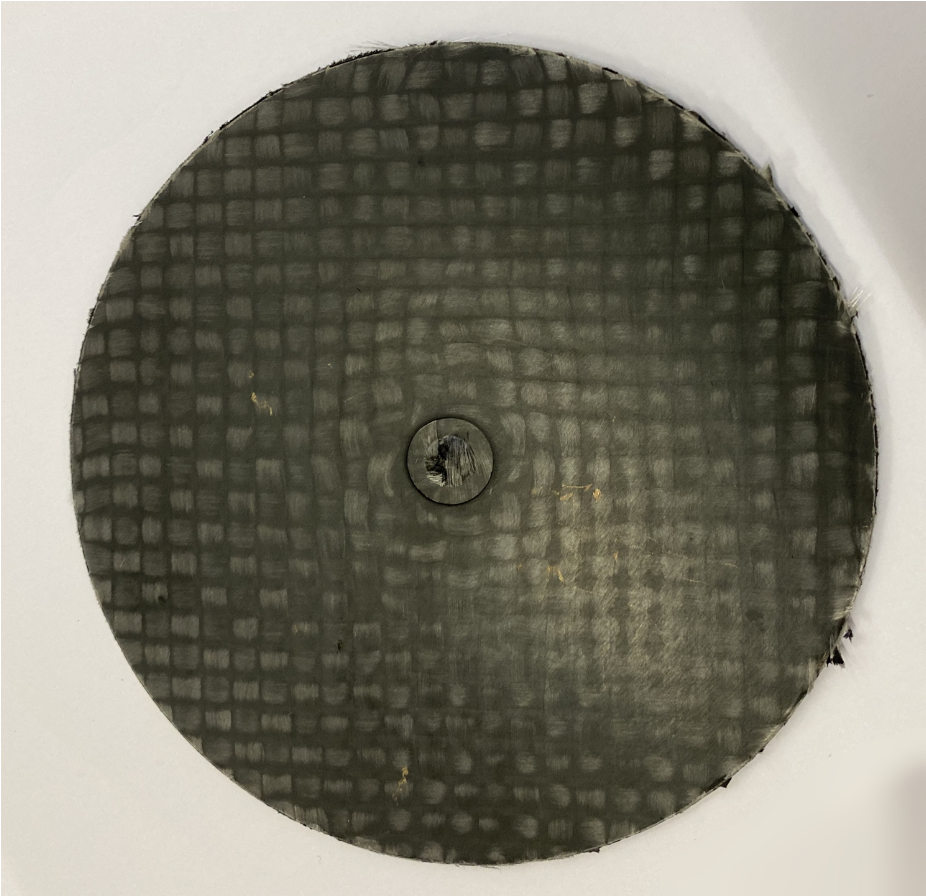
A novel tool with a variothermal sealing was designed and successfully implemented. Finite-Element analysis (FEA) was performed to define appropriate process parameters and to ensure sealing. Figure 3 shows the plates that were produced with the novel tooling with a diameter of 100mm and 2mm thickness. They display an elevated fibre volume fraction, advantageous mechanical properties and could be manufactured with a cycle time shorter than 10 minutes.
Execution | |
Duration | 4 years |
Funding | SCCER (Swiss Competence Center for Energy Research) 15916.1 PKOEN; Efficient Technologies and Systems tor Mobility, 2013-2020. |
Project team | Christian Rytka (lead), Halime Philipp, Yara Khalaf, Vincent Werlen, Daniel Zürcher, Oskar Häfeli, Stephanie Wegmann |