MSc Medical Informatics
Apply digital techniques and artificial intelligence in healthcare.
Key data
- Degree
- Master of Science in Medical Informatics
- ECTS points
- 90
- Studying mode
- Full- and part-time
- School days
- Monday to Saturday
- Duration
- 3 semesters (fulltime)
- Teaching language
- English
- Stay abroad
- optional
- Application fee
- CHF 200
The deadline for applications for the autumn semester is 30 April of the relevant year.
Mobile navi goes here!
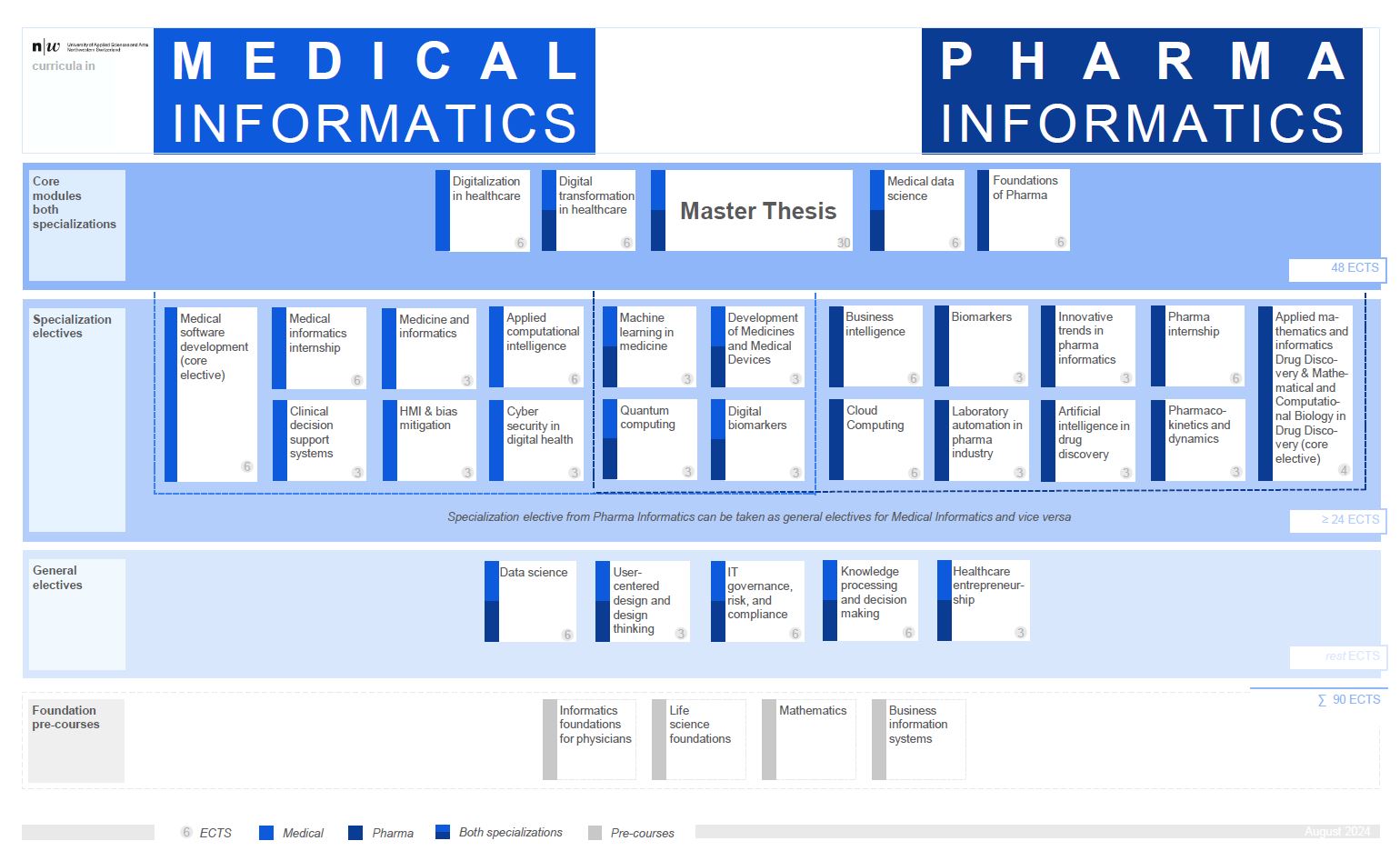
Two specialisations
Details
Core modules introduce the areas of computer science, healthcare and business, which are essential to operating successfully in the field of medical informatics. These modules are not offered in standard computer science courses. The four core modules offered are compulsory for all students:
- The core module Medical Data Science concentrated in how to apply cutting edge data science on medical data: alternative data sources, cleaning the data, statistics, visualization methods, predictive analysis, classical machine learning (ML), generative models, and the use of language machines such as chat GPT in medical informatics context.
- The Digital Transformation in Healthcare module covers the digital healthcare system. It provides a prospective on what is the impact of digital transformation across healthcare sectors from hospitals to the biopharmaceutical industry, regulatory agencies and ultimately patients.
- The development and use of software in the medical environment, either functioning as a medical device itself or as part of a medical device, is subject to specific rules and increasingly strict quality requirements. The core module Medical Software Development examines the international standards governing medical software development and how these are reflected in the day-to-day activities of a typical software development process.
- The Digitalization of Business Processes in Healthcare module provides an economic framework for the automation of processes as an interaction between humans and technology. The digitalization of business processes introduces this topic and establishes the business context. The module covers workflow management systems, their embedding in an organization and their interaction with various information systems.
- Foundations of Pharma: This course provides a comprehensive introduction to the foundational concepts of the path to new therapeutics, focusing on genetics, cell biology, human physiology, biopharmaceutics, and the processes involved in drug discovery and development.
- Applied Mathematics and Informatics in Drug Discovery (Uni Basel): This introductory course will offer a practitioner’s review of mathematical concepts, informatics tools, and industrial approaches in relevant fields, especially bioinformatics, molecular modelling, cheminformatics, mathematical modelling, experiment design and statistical inference, and machine learning.
Elective modules include lectures on medical informatics which explore application-oriented medical technologies and business lectures which examine the technologies in a business-oriented context.
The students choose elective modules from a range of medical informatics modules, business modules and other modules that consider the dynamic nature of the field of medical informatics in which the technologies and challenges are evolving rapidly and continuously. They enable content to react to current trends and priorities:
- Digital Biomarkers: This module covers the identification of digital indicators of a particular disease or physiological state of an organism.
- Applied Quantum Computing: This module gives an overview of the principles and applications of quantum computing in medicine.
- Development of Medicines and Medical Devices: This module gives an overview of the regulatory requirements, safety considerations, and ethical principles involved in drug development and clinical research.
- Innovation Trends in Medical Informatics (focus pharma): This module takes a seminar style approach to introducing innovative topics in medical informatics.
- Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery: This module covers artificial intelligence methods and algorithms applied to drug discovery.
- Machine Learning in Medicine: Applying machine learning techniques to different kind of medical data and applications. Medicine and Informatics.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems: Building tools designed to enhance healthcare providers' decision-making processes by offering evidence-based recommendations, real-time data analysis, and personalized patient insights.
- Medicine and Informatics (VR, AR and tech driven medicine): This course explores the transformative impact of informatics on modern medicine.
- Human Machine Interaction and Bias Mitigation: Creating and implementing responsible machine learning algorithms for healthcare that ensure fairness, accuracy, and inclusivity.
- Informatics of Pharmacometrics (Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics): The application of computational and statistical methods to model and analyze the effects, interactions, and behavior of drugs within the human body aiming to optimize drug development and therapeutic strategies.
- Applied Computational Intelligence: Students learn about Artificial Intelligence (AI) with a focus on Computational Intelligence (CI) and how to model, numerically simulate and optimise real-world problems on the computer
- (Genetic) Biomarkers: Students will be able to know the most important classes of biomarkers in cancer and other diseases, understand the process of biomarkers discovery, learn biomarkers in different diseases and know applications of biomarkers in clinical studies and diagnostics
- Cybersecurity in Health: This course on cybersecurity in healthcare examines the critical importance of protecting medical data and devices, highlighting the risks and challenges of cyber threats.
- Cloud Computing: The guiding principle of the module is to provide participants with the technical and management cloud skills of the future to help companies evaluate and use the cloud.
- Business Intelligence: Supporting business decisions with facts, by looking at different kinds of decisions, at different kinds of data and different kinds of tools required to distil information out of data.
- Laboratory Automation in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Basics in Cell Biology, Pharmacology and Cell Analytics
- Healthcare Entrepreneurship: Building a Successful Healthcare Venture
- Data Science: This module explores the prominent representatives from the artificial intelligence and machine learning area – including prominently the very popular neural networks.
- User-Centered Design and Design Thinking: The principles and methods to ideate and design technical systems for humans that are useable and effective, and their application in the context of health care.
- IT Governance, Risk and Compliance: Standards, frameworks, and best practices for a coordinated strategic and operational approach to running a business efficiently, with a focus on compliance, risk management, governance, and audit.
- Knowledge processing and decision making: Acquisition, representation, and inference of knowledge, either learnt by machines or explicitly acquired and represented, in order to make machines able to apply knowledge and support humans.
- Independent Learning: This module enables students to study any other relevant topics in medical informatics in more depth.
- Internship
Students who lack some of the prior knowledge required for the Master of Science in Medical Informatics will be offered pre-masters’ courses. These can be declared by the Admissions Committee as a prerequisite to starting the programme. The courses are offered in e-learning format and are free of charge.
There are four different courses offered:
- Digital Life Sciences - Overview of chemistry, molecular biology, biology, physiology, pharmacology, biotechnology, diagnostics, vaccines
- Programming (introduction to programming, data structures, algorithms, control structures, debugging, with examples from R, Python, and Java)
- Information Systems (introducing information systems, developing information systems - object-oriented principles with Java, modeling information systems - unified modeling language (UML))
- Mathematics
The master's thesis comprises 30 ECTS credits and is carried out during one semester in cooperation with external partner to allow students to get industry experience during their master thesis. Students work on challenging, application-oriented projects. They are supervised by a lecturer from the master's programme.
The programme can be pursued full-time or part-time alongside a related professional occupation. Both groups of students study together. The main difference is the duration of the course. The full-time programme generally takes 3 semesters, with 30 ECTS points awarded each semester. The part-time programme lasts 5 semesters, with 18 ECTS awarded each semester.
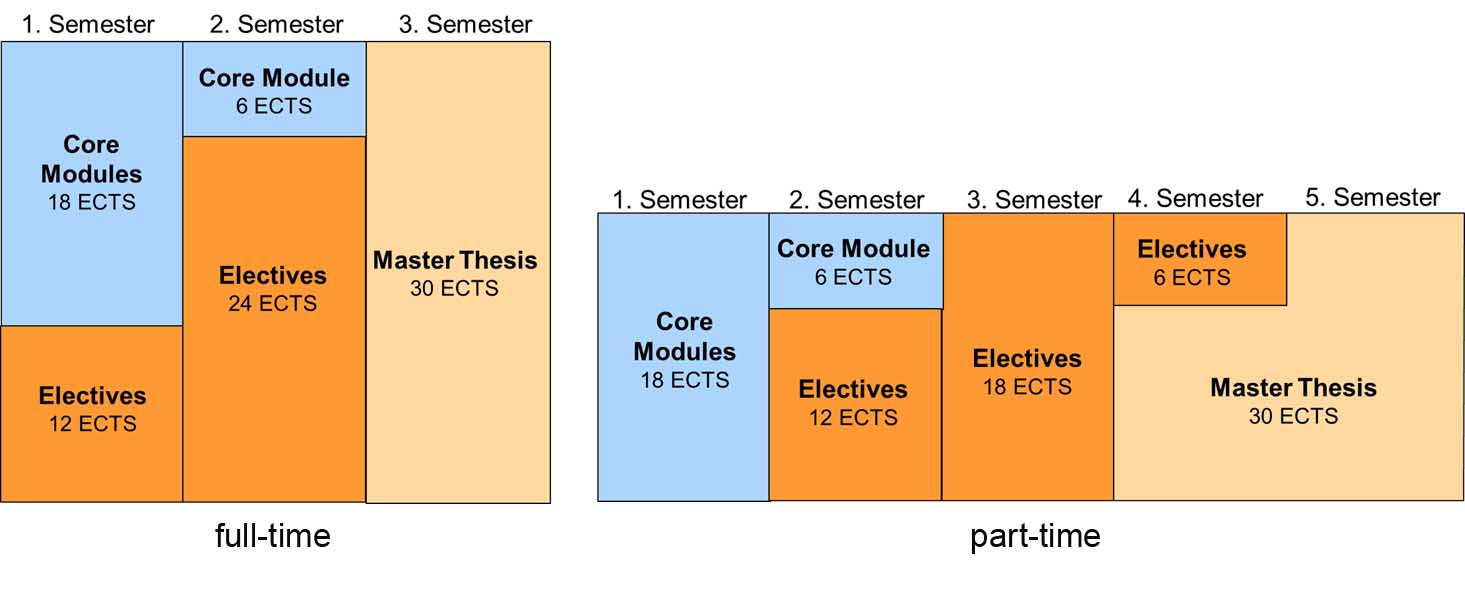
The programme structure is illustrated in the diagram. The students start by taking three core modules in the first semester. The elective modules are chosen freely. Students conclude their studies with their master's thesis.
The programme structure is illustrated in the diagram. The students start by taking three core modules in the first semester. The elective modules are chosen freely. Students conclude their studies with their master's thesis.
Type of certificate | Required Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
CEF | Common European Framework of Reference for Languages | C1 | ||
FCE | Cambridge First Certificate | FCE-A/B | ||
IELTS | International English Language Testing System | 5.5 | ||
TOEFL | Test of English as a Foreign Language | iBT 71 | ||
English III | Module of the bachelor's programme at the School of Life Sciences FHNW | 5.0 |
The master’s programme begins in the autumn semester (calendar week 38).
| CHF 750 | |
Tuition fees per semester for students who have their civil law residence in the EU/EFTA at the beginning of their studies | CHF 1000 | |
Tuition fees per semester for students who do not have their civil law residence in Switzerland or in an EU/EFTA state at the start of their studies. | CHF 5000 | |
A fee of CHF 100 per semester is also charged for materials and licences. | ||
The full semester fees are due if the deregistration or the exmatriculation application is not received by the FHNW within one week after the start of the semester. |
Prospects
Students will be working on current innovative projects at the interface between healthcare, computer science and economics. As a result, they will acquire knowledge in order to implement and develop digitalization in the health sector. As masters’ graduates they can take on tasks related to the application of artificial intelligence in drug discovery and personalized medicine, hospital information systems and economic processes. Possible employers are hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, federal institutions or insurance companies.
Admission
Designed for BSc graduates in Medical Informatics, as well as related disciplines such as Computer Science/Informatics, Medicine (MSc in Medicine or equivalent), Pharmaceutical Sciences , Life Sciences, or similar fields that meets the programming/medicine knowledge requirements.
Highly qualified graduates are admitted to the master’s programme if they:
- have acquired a Bachelor's degree in a relevant field with a grade of A, B, or ≥ 4.8 (≥ "good"),
- or possess an equivalent educational background and professional experience (college or university degree),
- and have successfully passed the interview,
- and demonstrate a very good command of the English language.
Pre-master’s courses are available for reflecting the required prior knowledge. Completion of these courses may be declared by the Admissions Committee as a prerequisite for starting the programme. These courses begin before the semester starts and are free of charge.