Medical Imaging
Segmentation with Level Sets.
Segmentation (i.e. delineation of anatomical structures in image data) plays a crucial role in medical imaging. Due to the complexity and variability of anatomic shapes, segmentation is still a big challenge.
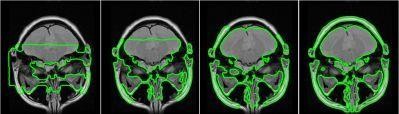
Contour propagation by initial conditions (40, 100, 150 and 200 iterations)
A wide variety of segmentation techniques have been proposed: a) traditional low-level image processing techniques which consider only local information and generate infeasible object boundaries and b) more robust techniques with deformable models which exploit constraints from the image data (bottom-up) together with “a priori” knowledge about the shape (topdown).
The Institute for Medical and Analytical Technologies is focusing in the field of Medical Imaging on Data-Visualization, -Analysis and Modeling. The study of segmentation techniques is therefore a fundamental issue.
For efficient and robust segmentation of various anatomic structures we implemented the Chan-Vese- algorithm (a deformable model with Level Sets).
The Chan-Vese algorithm is a deformable model approach with contour evolution based on the Mumford-Shah functional, and the level sets of Osher and Sethian.
First applications with specific anatomical structures (brain, vessels, spine) led to robust and accurate segmentation results. And a strength of the algorithm is its ability to handle the topology changes (level sets).
Due to the inability to distinguish between different shapes (no model-information) the algorithm is mainly useful for semi-automated segmentation.
This article is also available as PDF-file.