NanoCoat
Titanium and its alloys are the most frequently used biocompatible materials in medical engineering.
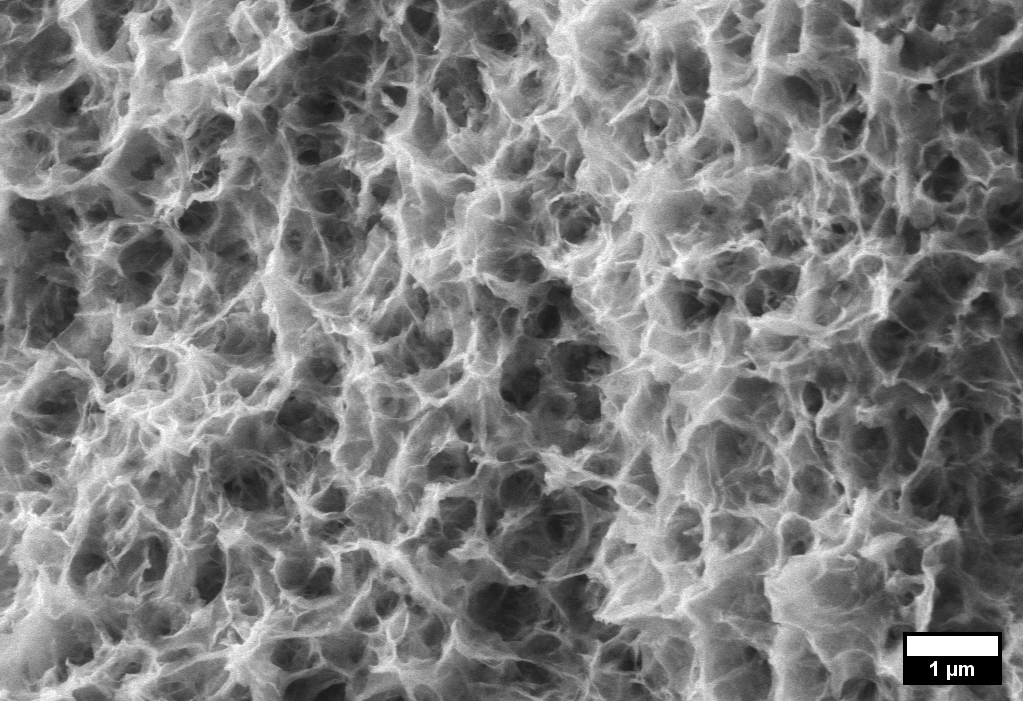
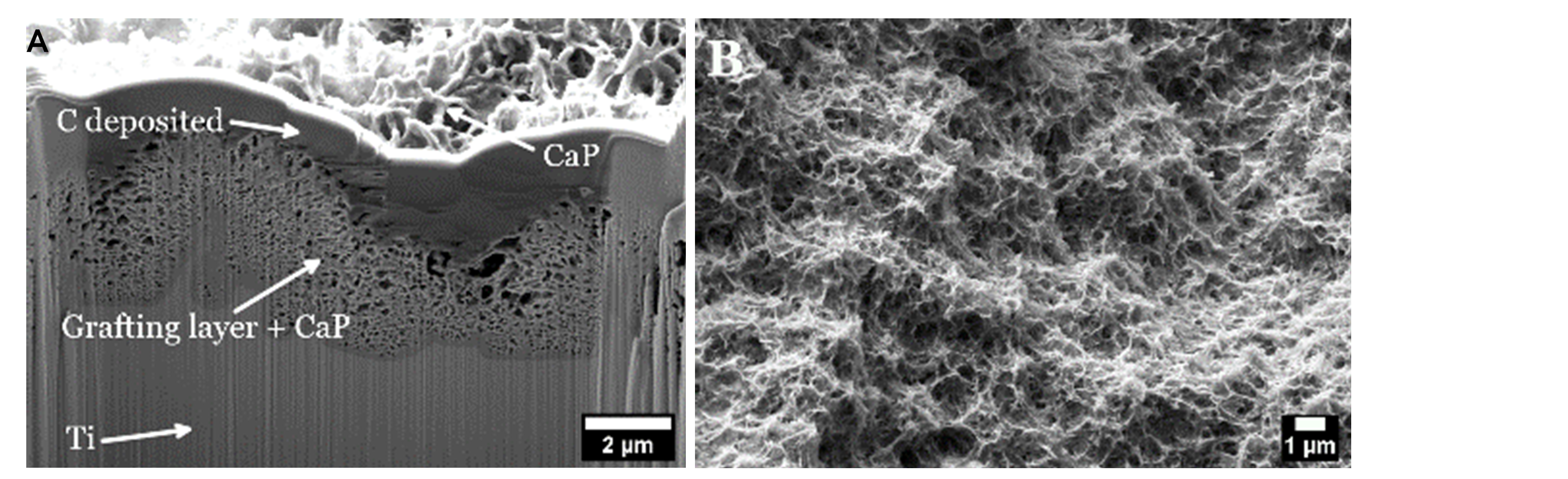
Accelerated osseointegration can be achieved by modifying the Ti surface with a layer of calcium phosphate (CaP). Current processes typically generate a relatively thick CaP (e.g., by plasma spray) and only a few thin coatings are available. We developed a cost-effective protocol for Ti surface modification with a thin CaP layer using a wet biomimetic route. The interface between implant and bone is one of the critical factors to achieve short healing time and long term stability. A ceramic micro- and nanostructured surface, strongly joined to the metal, is obtained.
- A. Testino, M. de Wild, E. Müller, A. Carino, F. Dalcanale, P. Gruner, W. Moser, Biomimetic growth of calcium phosphate ceramics on Ti implants, Annual Report 2018, Supplement, Swiss NanoScience Institute, University of Basel, Nano Argovia Project A13.09 NanoCoat, 90-91 (2018).
- A. Carino, A. Testino, E. Mueller, M. de Wild, F. Dalcanale, P. Gruner, W. Moser, B. Hoechst, Novel biomimetic approach for titanium surface treatment by calcium phosphate: Towards the production of implants with improved bioactivity, European Cells and Materials, Collection 4; SSB+RM Conference Abstracts (page 8) (2019).
- A. Carino, A. Testino, E. Mueller, M. de Wild, F. Dalcanale, P. Gruner, W. Moser, B. Hoechst, Implant surface modification by a controlled biomimetic approach, European Cells and Materials, Online Periodical, Collection 1; Meet the Expert Conference Abstracts, p2, (2019).